Table of Contents
Choosing between JPEG and PNG can sometimes feel confusing, especially when you’re trying to balance image quality, file size, and features like transparency. Whether you’re a photographer, graphic designer, or simply managing images for your website, understanding these two formats is key to making the right choice.
In this guide, we’ll dive deep into JPEG vs PNG, breaking down when to use each format and why it matters. Plus, we’ll cover practical tips on using these formats to get the best results, both online and in print.
Quick Summary
If you’re short on time, here’s a quick breakdown of when to use JPEG vs PNG:
- JPEG:
- Best for photos and images with lots of colours and details.
- Smaller file size thanks to lossy compression, ideal for websites and sharing.
- No transparency support.
- Perfect for web use when fast loading times matter.
- PNG:
- Best for logos, graphics, and images with transparency.
- Lossless compression keeps all the image data, ensuring high quality.
- Supports transparent backgrounds (perfect for web design).
- Ideal for design work and situations where image clarity is crucial.
Bottom line: Choose JPEG for smaller file sizes and photos, and choose PNG for high-quality graphics or when transparency is needed.
Let us continue with our in-depth analysis article.
Is JPEG and JPG same?
Yes, JPEG and JPG are the same. The only reason they have different names is due to file extensions. Back in earlier versions of Windows, file extensions were limited to three characters, hence the use of “.jpg” instead of “.jpeg.” Other operating systems like Mac and Linux didn’t have this limitation and used “.jpeg” for the full name.
But no matter what you call it, JPEG/JPG refers to the same image format and serves the same purpose.
Understanding JPEG and PNG
Before we dive into the comparison, let’s take a quick look at what each format is and what it’s best used for.
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
JPEG is one of the most widely used image formats on the web and in photography. It’s known for its ability to reduce file sizes through lossy compression. This means that some data from the image is lost during compression, but it allows you to create much smaller file sizes. However, this compression can cause a slight decrease in image quality, especially when you compress the image too much.
Key benefits of JPEG:
- Lossy compression: Smaller file sizes but at the cost of some image quality.
- Ideal for photos: Best for images with lots of detail and colour, like photographs.
- Widely supported: JPEG files work across nearly all platforms, devices, and websites.
- No transparency: JPEG doesn’t support transparent backgrounds, making it less suitable for web design and logos.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
It is a lossless image format which means it preserves all the original image data when compressed, ensuring that there’s no loss in quality. PNG files also support transparent backgrounds, making them perfect for logos, icons, and images that need to appear on different-coloured backgrounds seamlessly.
Key benefits of PNG:
- Lossless compression: Keeps all image data intact, preserving original quality.
- Transparency support: Allows for transparent and semi-transparent backgrounds (alpha channel).
- Great for web design: Especially for logos, icons, and UI elements.
- Larger file sizes: PNG files tend to be bigger than JPEGs due to their lossless compression.
Let’s Compare JPEGvs PNG
Here’s a basic comparison as can be seen in the picture.
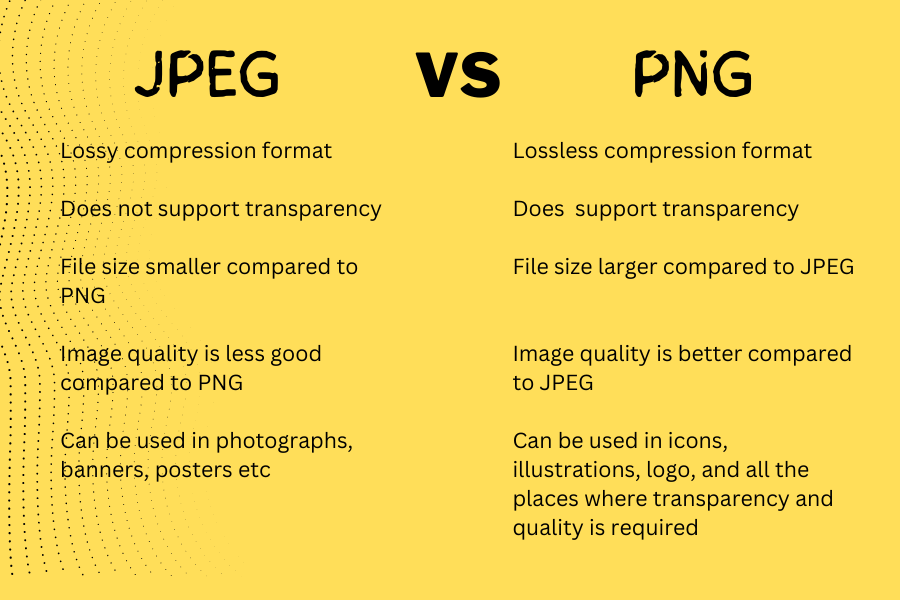
Let’s go to each topic one by one.
1. PNG vs JPEG Quality Assessment
When it comes to image quality, PNG stands out because of its lossless compression. This format keeps every detail of your image intact, no matter how many times you edit or save it. That’s why PNG is favoured for graphics, logos, and images where every pixel counts.
JPEG, however, uses lossy compression, meaning it reduces file size by discarding some data. While it’s fantastic for minimizing storage space, too much compression can make images blurry or pixelated, particularly when dealing with fine details.
Example: A logo saved as a PNG retains all its sharp edges and detail, while the same logo saved as a JPEG might appear slightly fuzzy, especially around the edges.
Takeaway: Use PNG when image clarity and precision matter. Use JPEG when a smaller file size is more important than perfect quality.
2. Transparency and Alpha Support
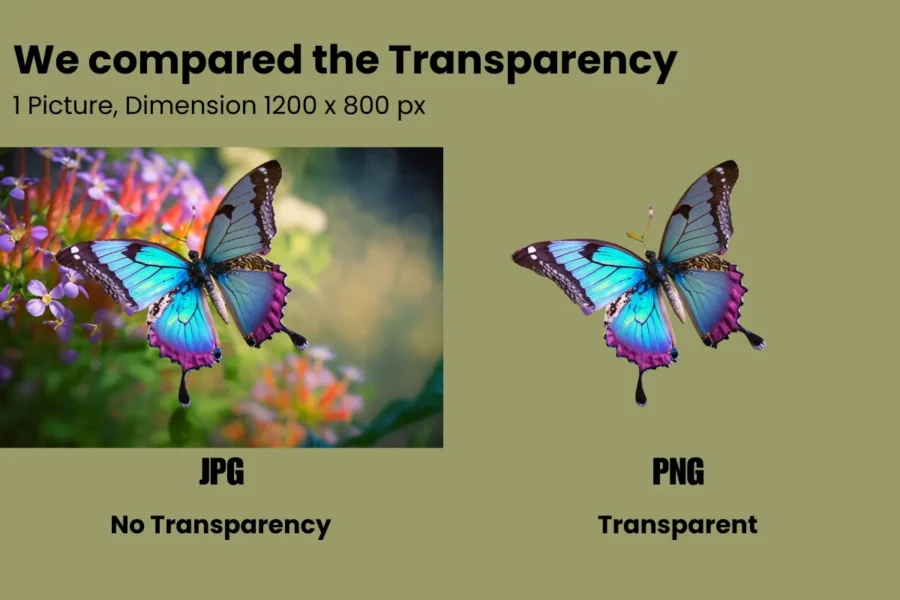
One of the biggest advantages of PNG over JPEG is its support for transparency. PNG files can have transparent or semi-transparent backgrounds, which is why they’re ideal for logos, icons, and web elements that need to sit on different backgrounds without showing a white or coloured box around them.
JPEG, on the other hand, doesn’t support transparency at all. If you need a transparent background, PNG is your best bet.
Example: A website logo saved as PNG can easily be placed over any background colour, while a JPEG logo will show up with a white (or coloured) box behind it.
Takeaway: Use PNG when you need transparent backgrounds. Choose JPEG when transparency isn’t required.
3. JPEG File Size vs PNG File Size

When it comes to file size, JPEG is the clear winner. JPEG files are significantly smaller than PNG files because of their lossy compression. This makes JPEG ideal for large collections of images, like those on websites or in galleries, where loading speed and storage space are priorities.
PNG files, while retaining more data, tend to be much larger. This can slow down websites and take up more storage space, making them less ideal for large image collections where file size is critical.
Takeaway: Use JPEG when you need smaller file sizes for web speed and storage. Use PNG when image quality is a higher priority than file size.
4. Lossless vs Lossy Compression
Lossless compression (PNG) ensures that no image data is lost during compression, preserving all of the original details. This makes it the perfect format for images that require a high degree of precision, like web graphics, logos, and charts.
Lossy compression (JPEG), on the other hand, reduces file size by discarding some data, which can affect the image quality. It’s great for reducing storage space but less ideal when you need to maintain the finest details of an image.
Takeaway: Use PNG for high-quality images with sharp edges and detail. Use JPEG for photos where file size is more important than perfect quality.
5. PNG vs JPEG for Editing
If you plan to edit and save an image multiple times, PNG is your best option. Since PNG uses lossless compression, the quality of your image won’t degrade, even after several edits. This makes it ideal for projects that require heavy editing or revisions.
JPEG, however, loses quality each time it is saved due to its lossy compression. This means that repeated edits can cause the image to look progressively worse over time.
Takeaway: Use PNG for images that need frequent editing. Use JPEG for images that won’t require much alteration.
6. PNG vs JPEG for Archiving
When it comes to archiving, PNG is generally a better choice. Its lossless compression ensures that no data is lost, which is important when storing high-quality graphics or logos that might need to be used again in the future.
JPEG is less ideal for archiving, especially for images you may need to re-edit or print later, as some quality is lost every time the image is saved.
Takeaway: Use PNG for archiving high-quality images. Use JPEG for casual archiving where minor quality loss is acceptable.
7. JPEG vs PNG for Printing
JPEG is often preferred for printing photographs because of its ability to handle complex colour variations and gradients while keeping file sizes smaller. For photos, JPEG will produce great results without the need for massive files.
However, PNG can also be used for printing, especially for graphics or images with text and sharp edges that require crispness.
Takeaway: Use JPEG for printing photographs. Use PNG for printing graphics with sharp lines and transparency.
8. JPEG vs PNG for Web Use
For the web, JPEG is usually the go-to format for photos, as its smaller file size ensures faster loading times. On the other hand, PNG is best for web elements like logos, icons, and graphics where you need transparency or a higher level of detail.
Takeaway: Use JPEG for website images where loading speed is crucial. Use PNG for logos, icons, and other design elements that require transparency.
Conclusion
To wrap up:
- Choose JPEG when file size is a concern, especially for web photos or when sharing large numbers of images.
- Choose PNG when image quality and transparency are essential, like for logos, web graphics, or when editing is involved.
Understanding the differences between JPEG and PNG will help you select the right format for your projects, ensuring you always get the best quality and performance from your images.
Frequently Asked Questions
For most photographs, JPEG is the better choice because it can handle complex colour variations while maintaining a smaller file size. However, for graphics with sharp edges or transparent backgrounds, PNG may produce better results, especially when fine details matter.
No, JPEG does not support transparency. If you need an image with a transparent background (for instance, a logo or icon), you should use PNG.
It depends on your needs:
JPEG is best for photos and large images where file size and fast loading times are important.
PNG is best for web elements like logos, icons, or images that require transparency or high-quality edges.
Lossless compression (used in PNG) retains all the image data when the file is compressed, meaning there’s no quality loss. Lossy compression (used in JPEG) reduces file size by discarding some data, which can slightly degrade the image quality.
Not necessarily. PNG is better for images where you need to retain every detail, such as graphics or images with sharp lines and text. JPEG can still offer excellent quality for photographs, especially when slight compression won’t be noticeable.
No. Converting a JPEG to PNG won’t restore any of the image quality lost during the JPEG’s initial compression. You’ll retain the same quality as the original JPEG, but the file size will likely increase due to PNG’s lossless format.
Professionals, such as photographers and graphic designers, often prefer PNG for archiving. Its lossless compression ensures that image quality remains intact, making it better suited for storing original graphics and designs. JPEG is better for archiving casual images or photos where small quality loss is acceptable.
For social media, JPEG is usually the preferred format because it provides a good balance between image quality and file size, making uploads faster and more efficient. However, for images that need transparent backgrounds (e.g., logos or overlays), PNG would be the better option.
Both PNG and JPEG work with the RGB colour model, which is best suited for digital screens. For printing, JPEG can be converted to CMYK for high-quality photo printing. However, PNG is not ideal for CMYK conversion, as it’s optimized for screen use rather than print.
Hope you liked this Tech Insights for more such articles. Also checkout